In the digital age, data is the bedrock of decision-making, innovation, and customer experience. As organizations scale and embrace more sophisticated data strategies, cloud databases have emerged as a critical solution.
Offering scalability, accessibility, and resilience, cloud databases are transforming how businesses store, process, and use their data. For enterprises engaged in cloud data processing, selecting the right database solution is pivotal to operational efficiency and unlocking the full potential of their data.
This article delves into the benefits of cloud databases, the considerations crucial for their implementation, and how organizations can make informed decisions about this transformative technology.
Table of Contents
Understanding Cloud Databases
Cloud databases are database systems hosted on cloud platforms, enabling organizations to administer and access data over the internet rather than relying on on-premise servers. Unlike traditional databases, which involve hefty investments in hardware and maintenance, cloud databases offer unparalleled flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Major providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide diverse cloud database services, ranging from transactional systems to expansive data warehousing. Complementing these offerings are tools like Skyvia, a versatile web service for cloud data integration, backup, and management. Skyvia enhances workflows, streamlines data access, and supports seamless integration across platforms, making it an invaluable resource for businesses adopting cloud databases.
Advantages of Cloud Databases
Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most compelling advantages is their inherent scalability. Businesses experiencing growth or fluctuations in demand can easily scale resources in real-time, ensuring efficient data management without overburdening budgets.
- Vertical Scaling: This approach involves increasing the database’s capacity by adding more powerful resources, such as CPU or memory, to a single instance.
- Horizontal Scaling: Horizontal scaling increases the number of database instances, distributing workloads to handle larger datasets and traffic.
This flexibility ensures that businesses pay only for the resources they use, avoiding the inefficiencies of over-provisioning or underutilization.
Cost-Efficiency
Cloud databases eliminate the need for costly investments in physical infrastructure, including servers, maintenance, and upgrades. The pay-as-you-go pricing model empowers organizations to align expenses with actual usage, making it a financially sound solution.
Moreover, cloud providers handle administrative tasks such as updates, backups, and security patches, reducing the need for an in-house IT team. This alleviates operational complexity and allows companies to redirect resources toward innovation and growth.
Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud databases enable universal access to data, facilitating collaboration across teams and geographies. This feature is particularly critical in today’s era of remote and hybrid work environments.
- Team members can work on data in real-time, ensuring synchronized efforts and faster decision-making.
- Developers can seamlessly integrate applications with cloud databases, accelerating project timelines and enhancing agility.
Such accessibility fosters a collaborative ecosystem where data-driven insights can fuel innovation and improve outcomes.
Considerations for Cloud Database Adoption

Despite their numerous advantages, cloud databases are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Businesses must evaluate their unique needs and challenges to ensure successful adoption.
Data Security and Compliance
Security remains a paramount concern when dealing with sensitive or mission-critical data. Key considerations include:
- Encryption: Data should be encrypted both at rest and in transit to protect against breaches.
- Compliance: Organizations must ensure that their chosen cloud provider adheres to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, depending on their industry and operational jurisdiction.
Solutions like Skyvia prioritize security with robust encryption and compliance features, giving businesses peace of mind in their data handling practices.
Performance Requirements
Different workloads demand varying levels of performance. Organizations should consider:
- Latency: For applications requiring real-time processing, selecting a cloud region closer to users can reduce latency and improve responsiveness.
- Storage Types: Depending on data structure and query needs, businesses can opt for SQL databases (structured data) or NoSQL databases (unstructured data).
By aligning database performance with workload requirements, organizations can optimize user experiences and operational efficiency.
Integration with Existing Systems
Seamless integration with existing infrastructure is crucial for businesses transitioning to cloud databases. Cloud databases must support interoperability with legacy systems, APIs, and third-party tools to ensure a smooth migration.
Advanced integration solutions like Skyvia simplify these processes, bridging the gap between on-premises systems and cloud platforms effectively.
Cloud Database Deployment Models
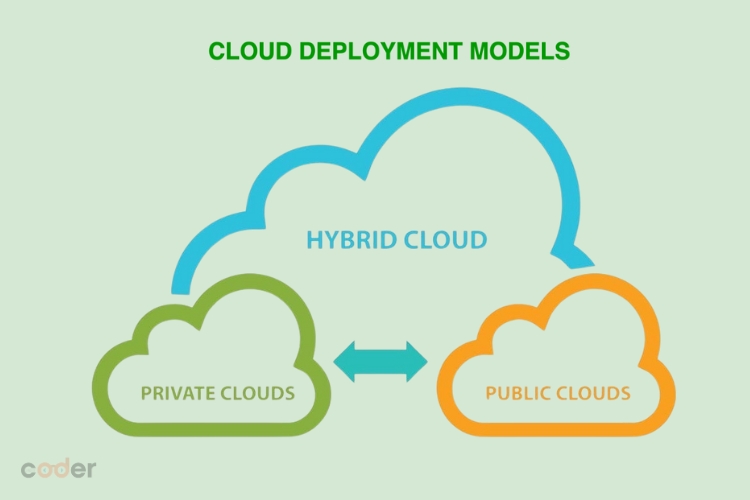
Businesses can choose from several deployment models when adopting cloud databases, each offering distinct advantages and limitations.
Public Cloud
In the public cloud model, multiple organizations share the infrastructure provided by the cloud provider.
- Pros: Affordable, highly scalable, and suitable for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Considerations: Limited control over infrastructure and potential security concerns.
Private Cloud
Private clouds provide dedicated resources, either on-premises or hosted by a third-party provider.
- Pros: Enhanced control, improved security, and customization options.
- Considerations: Higher costs compared to public cloud solutions, making them more suitable for large enterprises or industries with strict regulatory requirements.
Hybrid Cloud
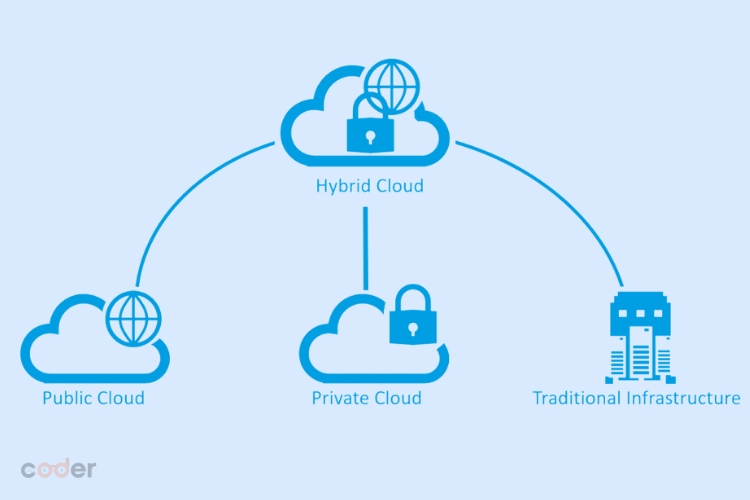
A hybrid cloud combines the strengths of public and private clouds. Organizations can store sensitive data in a private cloud while utilizing the scalability of public clouds for less critical workloads.
- Pros: Balances control with cost-efficiency, providing a versatile solution.
- Considerations: Requires robust integration and management strategies to maintain seamless operations.
The Role of Cloud Data Processing
Cloud data processing is central to leveraging cloud databases effectively. Advanced tools and platforms streamline these processes, enabling organizations to automate workflows, perform real-time analytics, and integrate data across multiple environments.
Choosing the right cloud data processing tools can significantly enhance the value derived from cloud databases. Tools like Skyvia simplify data management, offering capabilities such as automated workflows, intuitive integrations, and robust analytics. By capitalizing on these tools, businesses can unlock deeper insights and drive innovation.
Conclusion
Cloud databases represent a transformative shift in data management, offering scalability, cost-efficiency, and accessibility. However, their successful adoption requires careful planning and consideration of factors such as security, performance, and integration.
Solutions like Skyvia make working with cloud data processing seamless, enabling businesses to overcome challenges and fully embrace the advantages of cloud databases. As the digital landscape evolves, cloud databases will remain a cornerstone of innovation, empowering organizations to handle data with greater efficiency, resilience, and agility.
By leveraging the capabilities of cloud databases and complementary tools, businesses can build robust data strategies, ensuring they stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world.












![[SALE OFF] Discount 30% All Premium Extensions On Christmas And New Year 2025 christmas-and-new-year-2025](https://landofcoder.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/christmas-and-new-year-2025-1-218x150.png)






